Chromatin and gene-regulatory dynamics of the developing human cerebral cortex at single-cell resolution
Supplementary Online Resources
Abstract
Genetic perturbations of cerebral cortical development can lead to neurodevelopmental disease, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD). To identify genomic regions crucial to corticogenesis, we mapped the activity of gene-regulatory elements generating a single-cell atlas of gene expression and chromatin accessibility both independently and jointly. This revealed waves of gene regulation by key transcription factors (TFs) across a nearly continuous differentiation trajectory into glutamatergic neurons, distinguished the expression programs of glial lineages, and identified lineage-determining TFs that exhibited strong correlation between linked gene- regulatory elements and expression levels. These highly connected genes adopted an active chromatin state in early differentiating cells, consistent with lineage commitment. Basepair-resolution neural network models identified strong cell-type specific enrichment of noncoding mutations predicted to be disruptive in a cohort of ASD subjects and identified frequently disrupted TF binding sites. This approach illustrates how cell-type specific mapping can provide insights into the programs governing human development and disease.
Explore the data

Cell Explorer (Expression)
Explore the scRNA data in the cellxgene browser. The session includes cell anotation and normalized gene expression.
Explore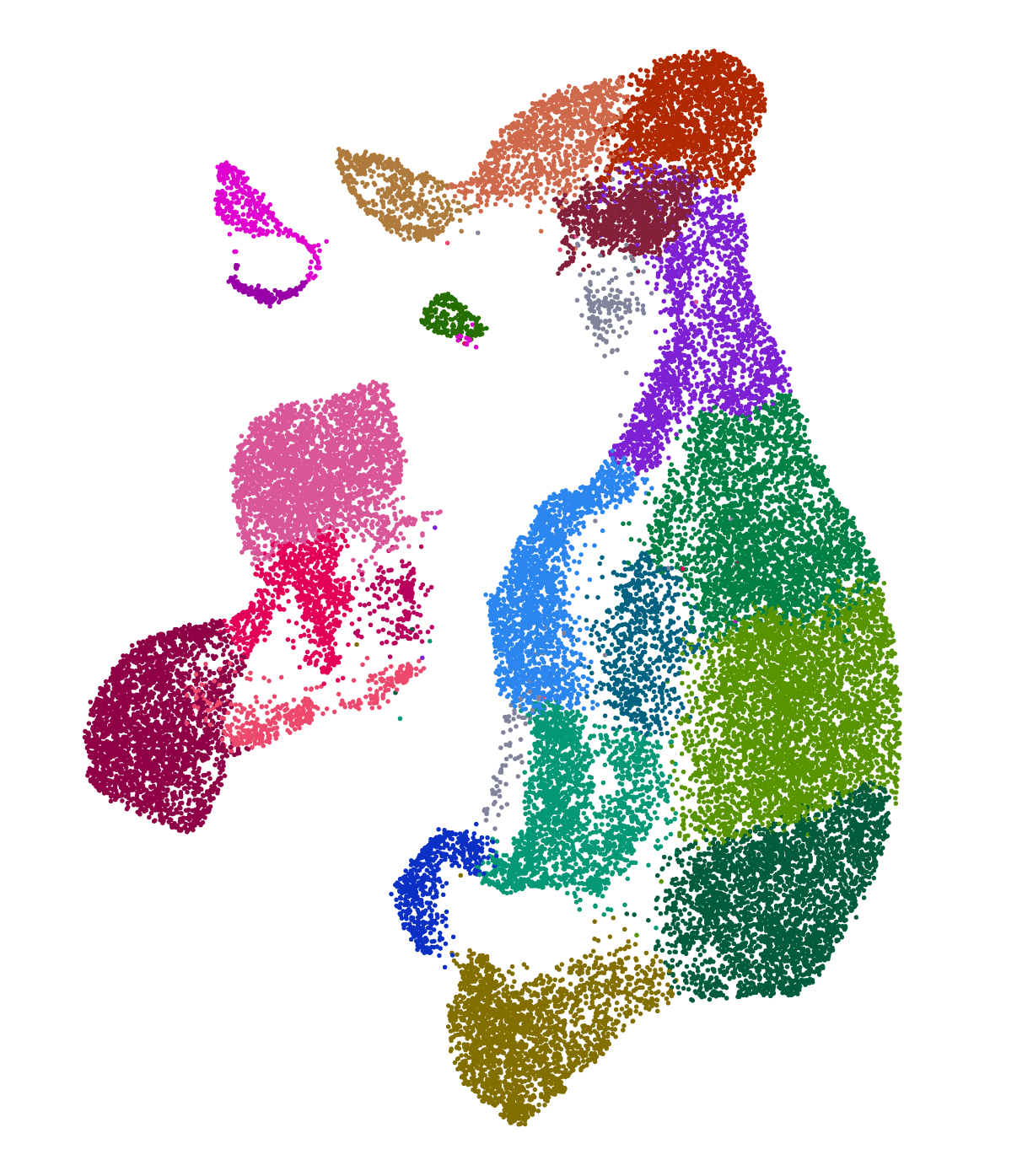
Cell Explorer (Chromatin)
Explore the scATAC data in the cellxgene browser. The session includes cell anotation and TF motif chromatin accessibility.
Explore
Data availability
Links to raw data archives and related resources.
| Repository | Reference |
|---|---|
| GEO | Super-series: GSE162170 |
| WashU Epigenome Browser Trackhub |
Browser session: Session Trackhub: JSON |
Code availability
Links to code repositories.
| Repository | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
brainchromatin |
Miscellaneous analysis scripts used to analyze scRNA and scATAC data. | GitHub |
Brain_ASD |
Repository contains scripts for training the neural network models used for prioritizing ASD mutations with the fetal brain ATAC-seq atlas. | GitHub |
ChrAccR |
R package for the analysis of chromatin accessbility data. Provides a pipeline and functions for the analysis of our scATAC data. | GitHub |
Citation
If you use this resource in your research, please cite:
Trevino*, A. E., Müller*, F., Andersen*, J., Sundaram*, L., Kathiria, A., Shcherbina, A., Farh, K., Chang, H. Y., Pasca, A. M., Kundaje, A., Pasca#, S. P., & Greenleaf#, W. J. (2021). Chromatin and gene-regulatory dynamics of the developing human cerebral cortex at single-cell resolution. Cell. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.039
© 2021; Greenleaf and Pasca labs at Stanford University; Site created by Fabian Müller